The essentials in 30 seconds
- The fertile window is a range, not a single day: it mostly sits before ovulation and ends on ovulation day.
- After ovulation, the egg is fertilizable for about 12 to 24 hours. NHS: Ovulation and the menstrual cycle
- In a large study, fertile days fell within a six-day window that ends on ovulation day. Wilcox et al., NEJM
- If you do not want to time it precisely, sex every two to three days usually covers the fertile window. NICE CG156
- If you do want to time it, cervical mucus helps you predict, LH tests give a short action window, and basal temperature confirms afterwards.
What is ovulation?
Ovulation is when a mature egg is released from an ovary. The egg travels into the fallopian tube, where fertilization can happen. A key point: ovulation is not always on cycle day 14. It depends on how long the first phase of your cycle is, and that can vary a lot.
A practical way to think about timing is the stretch before your next period. Ovulation often happens roughly 10 to 16 days before it, but that is a guideline, not a fixed date. NHS
How long are you fertile?
The fertile window is an interval, not one perfect day. The egg is only fertilizable for a short time after ovulation, while sperm can survive for several days. That is why the two days before ovulation and ovulation day itself are often the highest-probability days in studies. If you want the sperm numbers as a clear reference: How long do sperm survive?
Classic data from a large observational study show that pregnancies can largely be traced back to an approximately six-day window that ends on ovulation day. Wilcox et al., NEJM
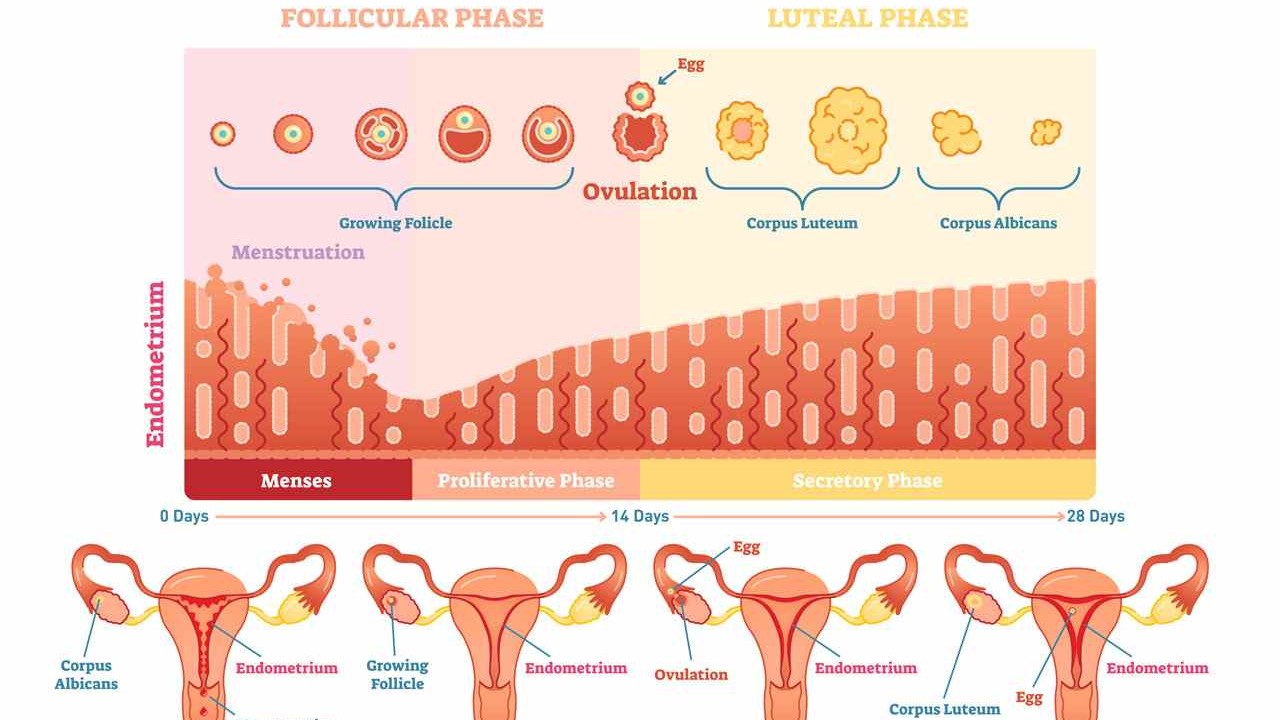
Cycle phases, in plain language
Many people want a number like day 12 to 16. That can fit, but it does not have to. In practice, it helps to understand the phases and then learn what your body tends to do.
- Menstruation: the uterine lining sheds. Hormones like estrogen and progesterone tend to be lower.
- Follicular phase: a follicle matures in the ovary. Estrogen rises and the lining builds up again.
- Ovulation: the egg is released.
- Luteal phase: after ovulation, progesterone helps keep the lining stable. If pregnancy does not occur, progesterone falls and the next period starts.
Calculating fertile days: what it can and cannot do
If your cycle is very regular, calculation can be a helpful rough framework. It is still only an estimate. Even small cycle shifts can move ovulation.
- Knaus-Ogino as a guide: first fertile day equals the shortest cycle minus 18, last fertile day equals the longest cycle minus 11.
- Reality check: even with 28-day cycles, not everyone ovulates on the same day. Think in intervals, not fixed dates.
Methods that genuinely work day to day
If you want to keep it practical, one principle helps most: cover the fertile interval without trying to hit a single perfect day. If you want to time it more tightly, combining prediction and confirmation is usually the most reliable approach.
Option 1: no tracking, still reliable
Sex every two to three days usually covers the fertile days well, without pinpointing ovulation. NICE CG156
Option 2: targeted timing with three signals
- Cervical mucus: helps with prediction. Clear, stretchy mucus often matches high fertility. How to read cervical mucus
- LH test: shows the LH surge that often signals ovulation in about 24 to 36 hours. LH surge and ovulation tests
- Basal temperature: confirms ovulation afterwards, since temperature typically rises after ovulation.
How to use an ovulation test correctly
- Start early enough. If you are unsure, start a few days earlier rather than missing the LH rise.
- Test around the same time each day and follow the manufacturer instructions.
- If the test turns positive, plan sex that day and the next day.
- If tests are often unclear or you stay positive for a long time, that can happen, for example with PCOS. In that case, interpretation matters. Understanding PCOS
If you need medical confirmation, a progesterone value in the second half of the cycle or an ultrasound can help. NICE CG156
Low-stress tracking: a 3-step plan
If you are just starting, less is often more. A simple two to three cycle plan usually brings clarity without turning every day into a project.
- Cover the interval. If you are actively trying to conceive, sex every two to three days is often enough to hit the window.
- Pick one prediction signal. Either track mucus or use LH tests. Using both is possible, but not required to learn your pattern. More on this: cervical mucus and LH tests
- Add one confirmation signal. Basal temperature works well here because the rise typically comes after ovulation. That lets you look back and see whether ovulation likely happened.
If you prefer tech, devices can help with logging, but they do not replace the logic of interval, prediction, and confirmation. Ovulation trackers compared
Typical signs: what fits and what is often overestimated
- Cervical mucus changes: many notice more moisture and clearer, stretchier mucus before ovulation.
- Mittelschmerz: mild one-sided lower abdominal pain can happen, but it is not reliable.
- Temperature rise: a small rise the next day fits better as confirmation, not prediction.
Many people do not feel clear signs. That is normal. Trust patterns over multiple cycles more than a single month.
After ovulation: what often changes
After ovulation, the cycle shifts into its second half. Hormones change. Some people notice nothing, others see familiar month-to-month patterns.
- Basal temperature: if you measure, you often see a rise that stays higher for several days. This is confirmation, not prediction.
- Body sensations: breast tenderness, more fatigue, or mood changes are common in the second half, but not specific.
- Mucus: many people feel drier again after the fertile peak. For everyday life, this is often the simplest sign that the window is closing.
If you are watching for implantation or early pregnancy signs, symptoms can look very similar. It often helps to think in days rather than interpreting every sensation. Implantation
If you are heading toward a pregnancy test, testing too early often just adds stress, because an early negative can later turn positive. Tested too early
If your second half is very short or you repeatedly have spotting, getting checked can be useful. Luteal phase issues
Ovulation myths and facts
- Myth: ovulation is always on day 14. Fact: the day varies, even among people with similar cycle lengths.
- Myth: no ovulation pain means no ovulation. Fact: many people feel nothing and still ovulate.
- Myth: basal temperature predicts ovulation. Fact: it confirms it afterwards.
- Myth: apps pinpoint ovulation exactly. Fact: apps estimate, and tests or body signs make timing more reliable.
- Myth: you are only fertile on ovulation day. Fact: the fertile interval starts earlier because sperm can survive for days.
- Myth: a negative LH test means ovulation is not happening. Fact: timing and test windows matter, and it is easy to miss the rise. How to interpret LH tests
Irregular cycles: when it is worth getting checked
If your cycle varies a lot, your period is absent for a long time, or tracking does not give a plausible picture of ovulation, a check-up can help. Common reasons include PCOS, thyroid issues, or sustained high physical or psychological stress. PCOS
In the US, a good starting point is an OB-GYN or your primary care clinician.
For general context on infertility and when medical support can be useful: WHO fact sheet on infertility.
Conclusion
Ovulation is not one perfect day, but part of a short fertile interval. If you want to keep it low stress, sex every two to three days usually covers the fertile days. If you want targeted timing, combine cervical mucus, an LH test, and basal temperature. If you feel unsure or your cycle is very irregular, medical testing is often the fastest way to get clarity.